Electromechanical Modelling of Switching Cell
The design of power electronic systems is typically performed with optimisation procedures, where analytical models of the system and its components are used. One important component of power electronic converter systems is the switching cell. A switching cell design consists of the semiconductor devices, the gate drivers, the DC-link capacitors, and the heat sink. The arrangement of these components has significant impact on the electrical and thermal performance of the converter.
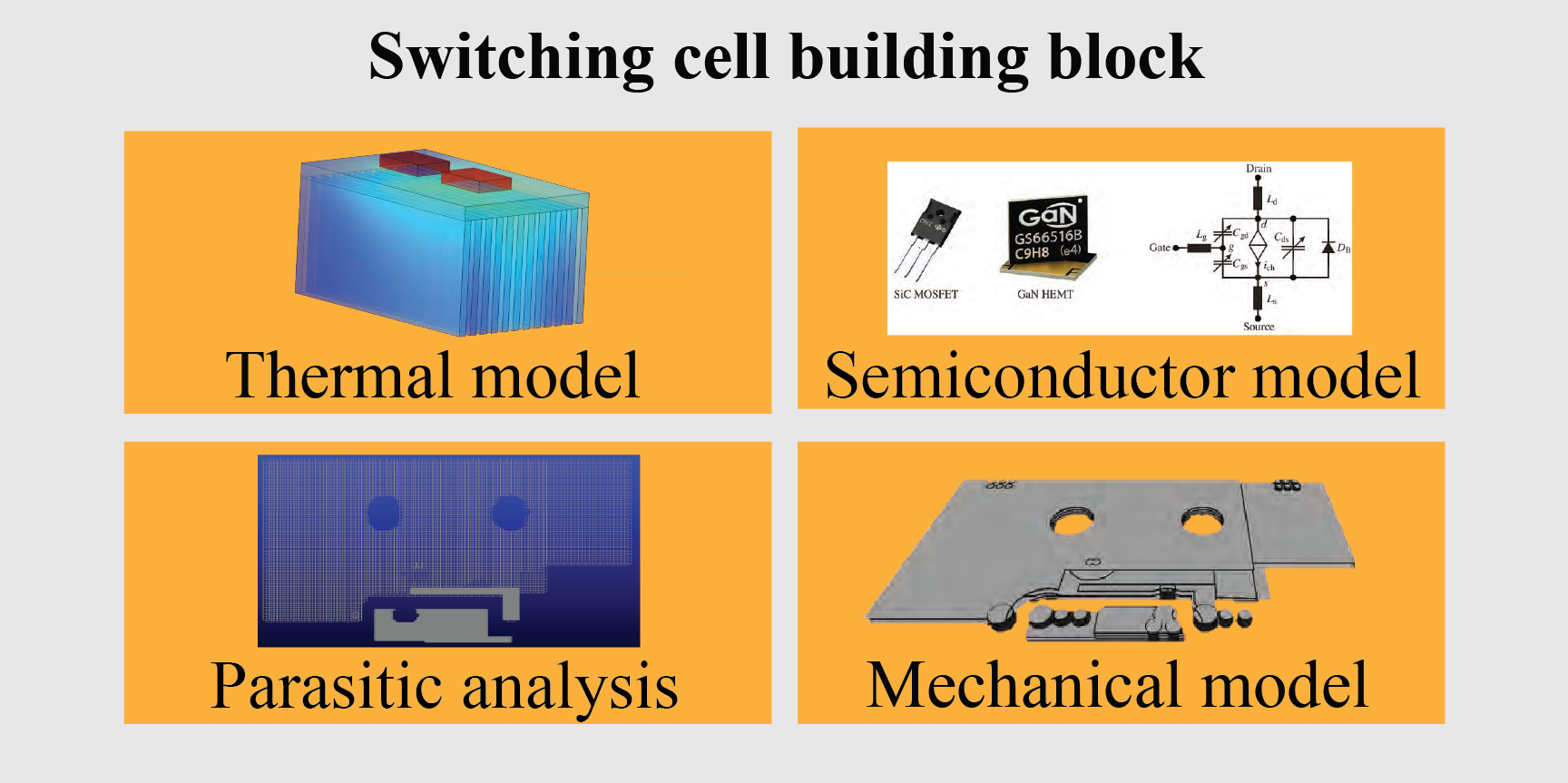
This project introduces the switching cell as an individual building block in converter system optimisation. The switching cell building block consists of several models to describe the electrical and thermal behaviour of the system. These models are the thermal models for estimating operating temperatures, taking into account the cooling system and thermal interactions between components, the models for estimating parasitic elements of the switching cell, and the models for calculating switching and conduction losses of the semiconductors. Additionally, a detailed 3D mechanical model is used to design a virtual prototype of the switching cell.
The aim of this project is to facilitate this virtual prototype and to automate the design process for power converter switching cells using a multi-objective optimisation tool. This tool considers component placement, layout parasitics and thermal coupling effects as design parameters. The automated design process incorporates temperature dependent component losses based on analytical modelling of thermal and electromagnetic coupling effects influenced by component placement on the heat sink and PCB layout.