HF-Loss Modelling in Litz Wire
Magnetic components such as medium frequency transformers or inductors are key components of modern power electronic systems. Because of the high-frequency effects, often Litz wire is used to reduce the winding losses. Litz wire consists of numerous strands which are twisted in a way that the bundle level high-frequency effects are cancelled. Numerical methods such as FEM are typically very time consuming, so that analytical models are preferred for calculating losses in LW in optimisation routines.
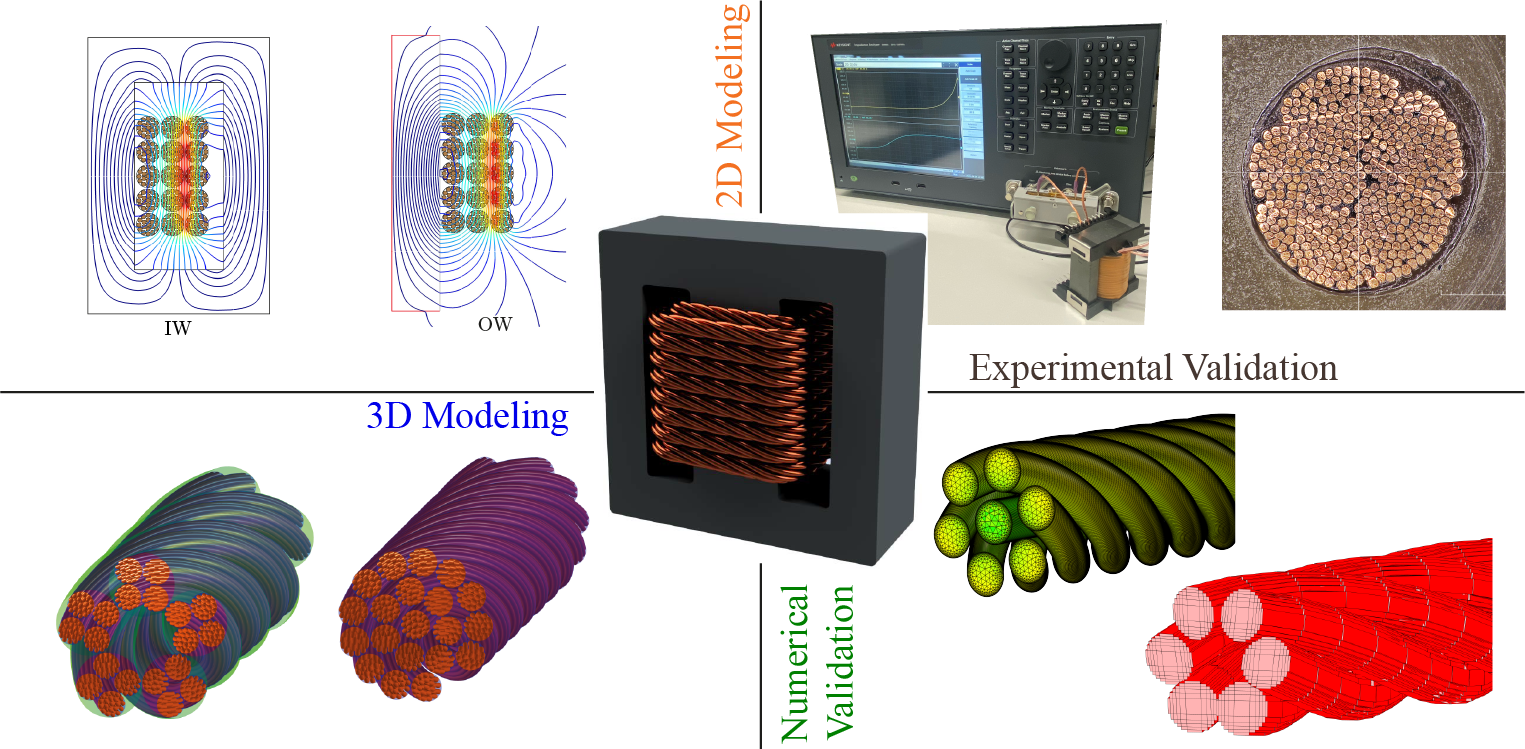
The existing analytical models are based on a perfect twisting and a 1D magnetic field assumption, which results in a relatively large error for the loss calculation. In typical transformers the winding height is usually lower than the window height due to isolation requirements and mechanical constraints, so that the magnetic field in the window is no longer 1D but 2D especially between the winding and the yoke. The project aims to develop a more accurate and computationally efficient model by considering the 2D magnetic field effects.
To evaluate the proposed models, winding loss measurements on transformer prototypes are designed and executed. The impact of the winding termination is also considered and studied. After the evaluation, an algorithm for fast loss calculation based on the proposed model is developed.